Before trying to answer the NCERT exercise questions, you should have a thorough understanding of class 7 Science chapter 8 i.e. ‘Reproduction in Plants‘.
If you haven’t understood the chapter yet, then worry not you can go through it easily and develop a crystal clear understanding of various concepts from our notes whose link has been provided below. ⤵️
NCERT Exercise Questions & Answers
Que. 1 Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of the parent is called_____________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called_____________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as________________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ________________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of ____________,________________ and ______________.
Ans. 1 (a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of the parent is called vegetative propagation.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as pollination.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed fertilisation.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of air, water and animals.
Que. 2 Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Ans. 2 Some of the common methods of asexual reproduction are:
Vegetative Propagation: New plants are produced from the vegetative parts of a plant like roots, stems, leaves, buds, etc.
Examples: roses are grown by cutting, potatoes from their eyes, Bryophyllum from their leaf buds, etc.
Budding: In this method of asexual reproduction the organisms are produced from the buds. A bud is a small bulb-like projection coming out of the parent’s body which detaches and forms a new organism.
Example: Yeasts reproduce asexually from budding.
Fragmentation: In this mode of reproduction the organism breaks into fragments after maturing and each of these fragments grows into a new organism.
Examples: Algae like Spirogyra and Ulothrix reproduce asexually by fragmentation.
Spore Formation: Spores are the asexual reproductive bodies that are covered in a protective coat and they are produced inside the sporangium of an organism. And when these spores find a suitable warm and damp environment they grow into a new organism.
Examples: Mainly the fungi (e.g. bread mould) and some plants like moss and ferns reproduce from the spore’s formation.
Que. 3 Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans. 3 In sexual reproduction there is a fusion of male gametes which are produced by the male reproductive organ(s) i.e. stamen (inside pollen grains) and the female gamete produced by the female reproductive organ i.e. pistil (inside ovule) resulting in a formation of new cell called zygote which matures into an embryo and later this embryo grows into a new organism which bears the characteristics of both male and female parent plants.
Que. 4 State the main differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans. 4 The main differences between asexual and sexual modes of reproduction are:
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| It requires only one parent. | It requires both the male and the female parents. |
| Progeny is identical to the parent. | Progeny is unique sharing characters of both the parents but also has some different characters altogether. |
| Special reproductive organs are not required. | Requires special reproductive organs for the gametes formation, transfer of gametes, maturation of zygote, etc. |
| Organisms like plants, yeast, hydra, algae, etc. reproduce by this mode of reproduction | Organisms like plants, animals, etc. reproduce by this mode of reproduction |
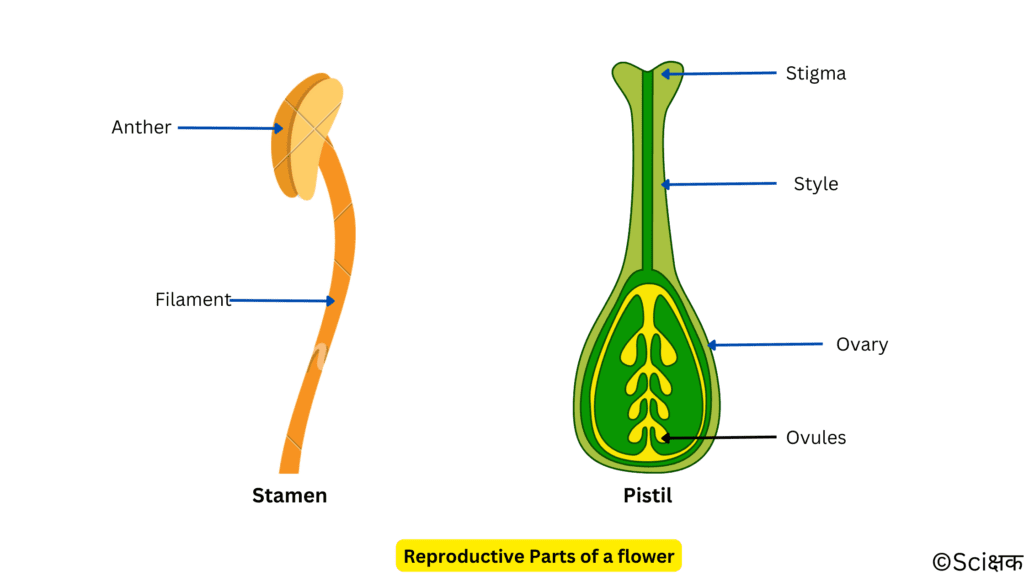
Que. 5 Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans. 5 A well-labelled diagram of the reproductive parts of a flower is given below:
Que. 6 Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Ans. 6 The main difference(s) between self-pollination and cross-pollination is:
| Self-pollination | Cross-pollination |
| The pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant. | The pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of the flower of a different plant of the same kind. |
| This type of pollination mainly takes place in bisexual flowers. | This type of pollination can take place in both the unisexual and bisexual flowers. |
Que. 7 How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Ans. 7 The pollen grains are brought to the stigma of the pistil via the pollinators. Then this pollen grain develops a pollen tube that runs through the style of the pistil to the ovary and then to the ovules. The male gametes that were present in the pollen grains now fuse with the female gamete present in the ovule of the ovary forming a zygote. This fusion is known as the fertilisation. Later, this zygote matures into an embryo. Ovules mature into seeds.
Que. 8 Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Ans. 8 The seeds of a plant can be dispersed over a large area by various entities:
SEED DISPERSAL BY AIR (ANEMOCHORY):
Examples:
- Winged seeds of maple and drumstick.
- Light seeds of grasses.
- Hairy seeds of aak or madar.
- Hairy fruit of the sunflower, etc.
Such seeds or fruits enclosing the seeds get blown off by wind to far away places.
SEED DISPERSAL BY WATER (HYDROCHORY):
These seeds or fruits enclosing the seeds develop floating ability in the form of a spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut.
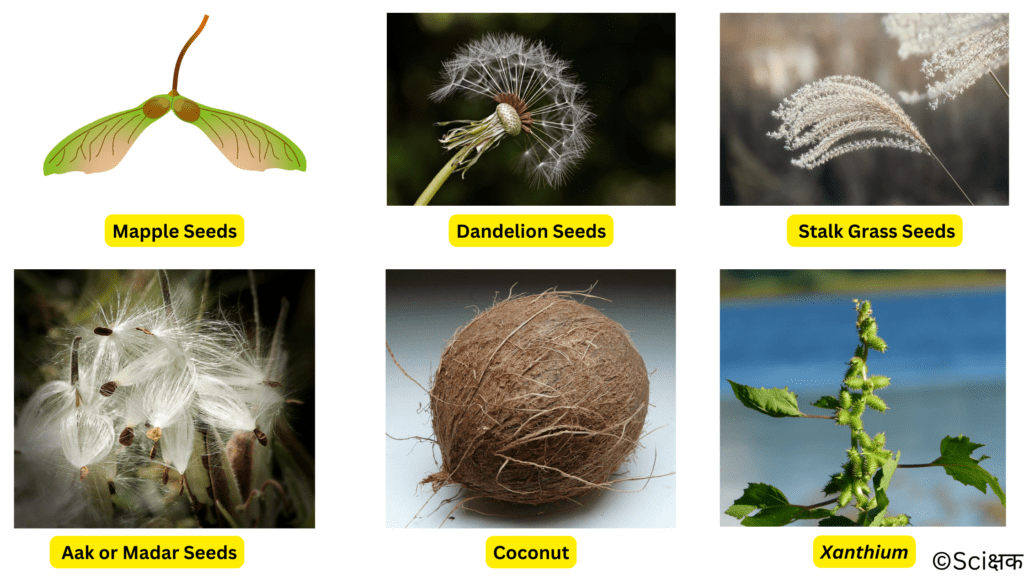
SEED DISPERSAL BY ANIMALS (ZOOCHORY):
Seeds that are spiny and have hooks get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places.
E.g. Xanthium (Cockleburs) and Urena
Special Mechanism of Seed Dispersal (BALLISTIC DISPERSAL):
In plants like castor and balsam, the fruits burst open with a sudden jerk spilling their seeds over large distances.
Que. 9 Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | ii) Spirogya |
| (c) Fragmentation | iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | iv) Bread mould |
| (e) Spores | v) Potato |
| vi) Rose |
Ans. 9 The correctly matched items of Column I with Column II are:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bud | iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | v) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | ii) Spirogya |
| (d) Wings | i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | iv) Bread mould |
Que. 10 Tick (✔️) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the:
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing organism is
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem
(ii) leaves
(iii) roots
(iv) flower
Ans. 10 (a) (iv) flower
(b) (i) fertilisation
(c) (iv) fruit
(d) (ii) bread mould
(e) (ii) leaves
Credits & References
- Class 7th Science NCERT Textbook
- Image by hartono subagio from Pixabay
- canva.com
- Image by David Ehret from Pixabay
- Image by Heike Tönnemann from Pixabay
- Image by JamesDeMers from Pixabay
- Image by Daina Krumins from Pixabay
- Image by Hans from Pixabay
Thank You for Choosing Sciक्षक ❤️

