Before trying to answer the NCERT exercise questions, you should have a thorough understanding of class 7 Science chapter 4 i.e. ‘Acids, Bases and Salts‘.
If you haven’t understood the chapter yet, then worry not you can go through it easily and develop a crystal clear understanding of various concepts from our notes whose link has been provided below. ⤵️
NCERT Exercise Questions & Answers
Que. 1 State differences between acids and bases.
Ans. 1 The differences between acids and bases are:
| Acids | Bases |
| These substances are sour in taste | These substances are bitter in taste |
| They are not soapy in feel | They are soapy in feel |
| They turn Blue litmus to Red | They turn Red litmus to Blue |
| They don’t change the colour of turmeric | They change the colour of turmeric to red |
| e.g. citric acid, sulfuric acid, etc. | e.g. milk of magnesia, sodium hydroxide, etc. |
Que. 2 Ammonia is found in many household products, such as window cleaners. It turns red litmus blue. What is its nature?
Ans. 2 Ammonia that is found in many household products like window cleaners that turn red litmus blue is basic in nature because only bases turn red litmus to blue.
Que. 3 Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution?
Ans. 3 Litmus solution is obtained from lichens. This is used as an acid-base indicator. It gives different colours in both acidic and basic solutions, helping us to differentiate between the acidic and basic substances.
Que. 4 Is the distilled water acidic/basic/neutral? How would you verify it?
Ans. 4 Distil water is actually neutral in nature and it can easily be verified by using red and blue litmus papers. In either of the cases, the colour of the litmus remains unchanged.
Que. 5 Describe the process of neutralisation with the help of an example.
Ans. 5 When we mix an acidic solution with a basic solution the neutralisation reaction takes place producing salt and water.
An acid and a base are anti of each other meaning they cancel out each other in a solution. So if we mix hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide base (NaOH) together, they will react together and produce salt (Sodium chloride, NaCl) and water (H2O).
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide ————-> Sodium chloride + Water + heat
HCl + NaOH ———-> NaCl + H2O + heat
Que. 6 Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) Nitric acid turns red litmus blue. (T/F)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus red. (T/F)
(iii) Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid neutralise each other and form salt and water. (T/F)
(iv) An indicator is a substance that shows different colours in acidic and basic solutions. (T/F)
(v) Tooth decay is caused by the presence of a base. (T/F)
Ans. 6 (i) Nitric acid turns red litmus blue. (F)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus red. (F)
(iii) Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid neutralise each other and form salt and water. (T)
(iv) An indicator is a substance that shows different colours in acidic and basic solutions. (T)
(v) Tooth decay is caused by the presence of a base. (F)
Que. 7 Dorji has a few bottles of soft drinks in his restaurant. But, unfortunately, these are not labelled. He has to serve the drinks on the demand of customers. One customer wants an acidic drink, another wants a basic and the third one wants a neutral drink. How will Dorji decide which drink is to be served to whom?
Ans. 7 Dorji can differentiate between the bottles of soft drinks either by tasting a small amount of the cold drinks or with the help of an acid-base indicator like litmus paper.
- Dorji can take a tasting sip out of each bottle and differentiate the cold drinks. The acidic soft drink will be sour in taste, the basic soft drink will be bitter in taste and the neutral soft drink will be tasteless.
- Or, he can use a litmus paper test. He can take out a few drops of each soft drink in three separate glasses and then dip the blue and red litmus paper in each one of them. The soft drink that would turn blue litmus to red is acidic, the soft drink that would turn red litmus to blue is basic and the soft drink that will not turn either of the litmus paper is neutral.
Once, the soft drinks are differentiated they can be served to their respective customer.
Que. 8 Explain why:
(a) An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity.
(b) Calamine solution is applied on the skin when an ant bites.
(c) Factory waste is neutralised before being disposed it into the water bodies.
Ans. 8 (a) An antacid tablet is basic in nature and we take it when we suffer from acidity. It neutralizes the excess of acid in our stomach and provides us relief.
(b) Calamine or zinc carbonate is a basic solution and it is applied on the skin when an ant bites. An ant bite contains formic acid and calamine neutralizes this acid providing us relief.
(c) Factory waste is mostly acidic in nature and it has to be treated or neutralized (with a basic solution) before being disposed into the water bodies because this acidic factory waste can harm or kill the aquatic life and pollute the water.
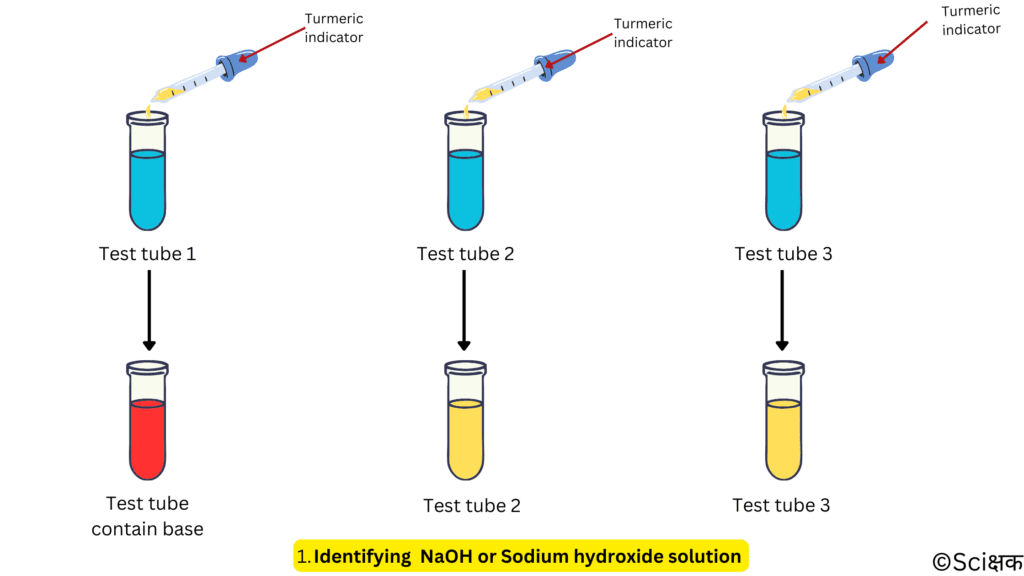
Que. 9 Three liquids are given to you. One is hydrochloric acid, another is sodium hydroxide and the third is a sugar solution. How will you identify them? You have only a turmeric indicator.
Ans. 9 Well there are two methods with which we can identify the hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and a sugar solution just by using a turmeric indicator.
Identifying NaOH or Sodium hydroxide solution:
- Take a few drops of each of the solutions into three separate test tubes.
- Now, add a few drops of turmeric indicator to each one of them.
- The solution that will change the colour of the turmeric indicator from yellow to red is basic or sodium hydroxide.
- Don’t throw this red colour base-turmeric solution as we’ll use it in our second method.
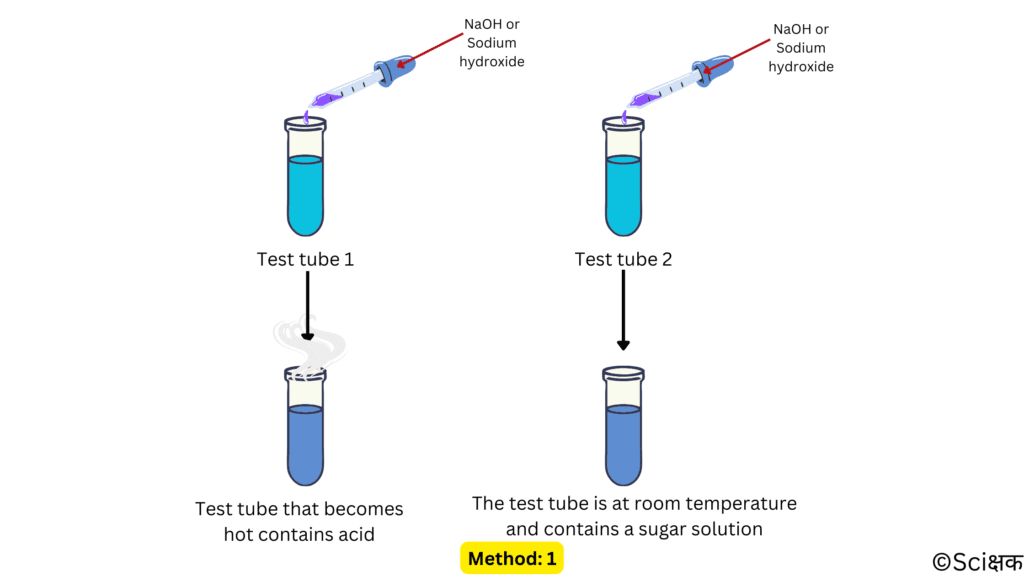
Now that we have identified the NaOH solution we’ll identify the remaining two (hydrochloric acid and a sugar solution and for that we have two separate procedures):
METHOD: 1
- Take a few drops of the remaining two solutions into two separate test tubes.
- Now, add a few drops of sodium hydroxide to each of the tubes and stir them gently.
- Now, carefully touch the bottom of the test tubes.
- The test tube whose bottom has become a bit warmer contains hydrochloric acid because a neutralisation reaction is taking place in it that is producing heat. And, the test tube which is still at room temperature contains the sugar solution.
- And, This way we can identify the hydrochloric acid and a sugar solution.
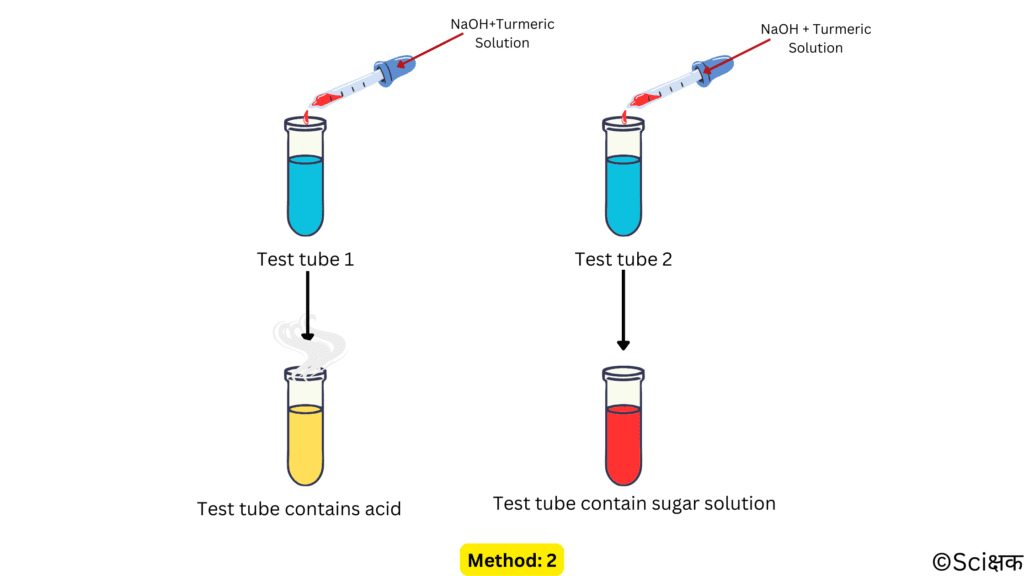
METHOD: 2
- Take a few drops of the remaining two solutions into two separate test tubes.
- Now, add a few drops of the red colour base-turmeric solution in each of the test tubes and stir the content gently.
- The sugar solution will gain a reddish colour as it will not react with the base-turmeric solution.
- But, the hydrochloric acid solution will turn the red-coloured base-turmeric solution back to yellow in colour by neutralising the base.
Que. 10 Blue litmus paper is dipped in a solution. It remains blue. What is the nature of the solution? Explain.
Ans. 10 If we dip a blue litmus paper in a solution and it remains blue then it is either basic in nature or neutral in nature.
Que. 11 Consider the following statements:
(a) Both acids and bases change the colour of all indicators.
(b) If an indicator gives a colour change with an acid, it does not give a change with a base.
(c) If an indicator changes colour with a base, it does not change colour with an acid.
(d) Change of colour in an acid and a base depends on the type of the indicator.
Which of these statements are correct?
(i) All four
(ii) a and d
(iii) b, c and d
(iv) Only d
Ans. 11 (iv) Only the d statement is correct. The change of colour in an acid and a base depends on the type of the indicator
References & Credits
- Class 7th Science NCERT Textbook
- Image by David Hablützel from Pixabay
Thank You for Choosing Sciक्षक ❤️

