Introduction
Before trying to answer the NCERT exercise questions, you should have a thorough understanding of class 7 Science chapter 3 i.e. ‘Heat‘.
If you haven’t understood the chapter yet, then worry not you can go through it easily and develop a crystal clear understanding of various concepts from our notes whose link has been provided below.
NCERT Exercise Questions & Answers
Que. 1 State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans. 1 The similarities between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer are:
- Both are made up of long, narrow and uniform glass tubes.
- Both have a bulb filled with mercury present at one end.
- Both are marked with a scale of either Celcius or Fahrenheit.
The differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer are:
| Laboratory Thermometer | Clinical Thermometer |
| It is used to measure the temperature of objects other than the human body. | It is used to measure the temperature of the human body. |
| The temperature range that it can measure is usually from -10°C to 110°C | The temperature range that it can measure is usually from 35°C to 42°C. |
| It doesn’t have a kink present in it. | It usually has a kink present in it that prevents the immediate fall in the mercury level while measuring the body temperature. |
Que. 2 Give two examples of each conductor and insulator of heat.
Ans. 2 Examples of the conductor of heat are iron, copper, aluminium, etc.
Examples of heat insulators are air, water, rubber, wood, etc.
Que. 3 Fill in the blanks:
(a) The hotness of an object is determined by its_________________.
(b) Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a ______________ thermometer.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree _____________.
(d) No medium is required for the transfer of heat by the process of ____________.
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. Heat is transferred to its other end by the process of ____________________.
(f ) Clothes of _____________ colours absorb more heat better than clothes of light colours.
Ans. 3 (a) The hotness of an object is determined by its temperature.
(b) The temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a clinical thermometer.
(c) Temperature is measured in degrees Celcius or Fahrenheit.
(d) No medium is required for the transfer of heat by the process of radiation.
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. Heat is transferred to its other end by the process of conduction.
(f ) Clothes of dark colours absorb more heat better than clothes of light colours.
Que. 4 Match the following:
| I) The Land breeze blows during | (a) Summer |
| II) The sea breeze blows during | (b) Winter |
| III) Dark-coloured clothes are preferred during | (c) Day |
| IV) Light-coloured clothes are preferred during | (d) Night |
Ans. 4 The correct match of the items given is:
| I) The Land breeze blows during | (d) Night |
| II) The sea breeze blows during | (c) Day |
| III) Dark-coloured clothes are preferred during | (b) Winter |
| IV) Light-coloured clothes are preferred during | (a) Summer |
Que. 5 Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing.
Ans. 5 Wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing because layers of clothes have air trapped between them and air being a heat insulator doesn’t allow heat to escape from our body to the surrounding, hence keeping us warmer.
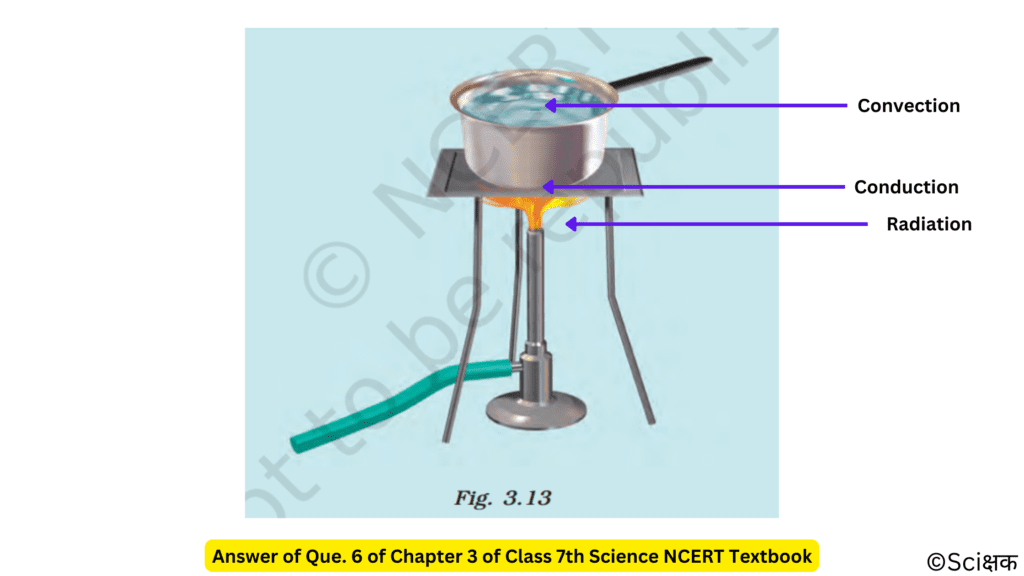
Que. 6 Look at Fig. 3.13. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.
Ans. 6 The places where the heat is being transferred by conduction, convection and radiation are:
Que. 7 In places of hot climate, it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Ans. 7 In places of hot climates like in Northern India it is advised that the outer walls of houses should be painted white because the white colour is a good reflector of light and heat and it is a very poor absorber of heat. So, most of the heat will be reflected, keeping the house cooler.
Que. 8 One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be:
(a) 80°C (b) more than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C (d) between 30°C and 50°C
Ans. 8 (d) Between 30°C and 50°C because one litre of water at 50°C will lose heat whereas one litre of water at 30°C will absorb that heat.
Que. 9 An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will
(a) flow from the iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
Ans. 9 (b) The heat will not flow from the iron ball to water or from water to the iron ball because both entities are at the same temperature.
Que. 10 A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) does not become cold.
Ans. 10 (d) Its other end does not become cold as wood is a bad conductor of heat.
Que. 11 Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) such pans appear colourful.
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel.
(d) copper is easier to clean than stainless steel.
Ans. 11 (c) Because copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel.
References & Credits
- Class 7th Science NCERT Textbook
- Image by Gylfi Gylfason from Pixabay
Thank You for Choosing Sciक्षक ❤️

