Table of Content
Introduction
So, what did you have for lunch at your school today?

Depending upon your location you could have had a different variety of food items like roti, sabji, dahi, rice, curry, fish, etc. No matter where you live in India your diet definitely consists of at least one item made up of grains (edible seeds like wheat, rice, etc.). We all have this enormous variety in the food that we consume.

But have you ever wondered, what’s the need for having such a vast variety of food?
Well if not then you are in for a treat, in this chapter we are going to deep dive into this question.
What Do Different Food Items Contain?
Before going into this topic, I have a small task for you all. Today, you have to observe how your parents/caretakers prepare the food (breakfast, lunch, and dinner). Observe them keenly and note down the items that they use while cooking.
We consume food because we don’t want to die as simple as that, but what’s in the food that’s keeping us all alive and healthy?
Well, the components of the food that keep us alive, healthy, and happy as well are known as Nutrients.
Major Food Nutrients
- Carbohydrates
- Protein
- Fat
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Dietary Fibres or Roughage
- Water
But, how would we know whether our food contains these nutrients?
Well, we are going to test their presence in our food with some simple methods and chemicals.
We can easily check for the presence of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in our food but for the rest of the nutrients, it’s quite difficult to check their presence.
Test for Carbohydrate (Starch)
What is this starch?
Starch is stored carbohydrates in plants that we consume. Rice, wheat, and potato are good sources of starch.
Things we need for this test –
- Food items e.g. rice, potato, pulses, fruits, etc.
- Dilute iodine solution (prepared by mixing a few drops of tincture iodine in a test tube filled with water).
What’s a dilute solution?
It means mixing a small amount of a chemical in a large amount of water or alcohol.
e.g. similar to mixing a few drops of milk or ink in water.
The Opposite of a dilute solution is a concentrated solution in which we mix a large amount of a chemical in a small amount of water or alcohol.
Fun Fact: Tincture iodine is antiseptic in nature just like Dettol.
How to Test for Starch –
- Take a small amount of food item.
- Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it.
- Observe if there is any change in the color of the iodine that we put onto the food item.
Observations & Inferences –
If the color of the food item changes to blue-black, then it confirms the presence of starch in our food.
Test for Protein
Things we need for the test –
- Food items.
- Test tubes.
- water.
- Copper sulphate solution (prepared by dissolving 2g of it in 100 mL of water).
- Caustic soda (prepared by dissolving 10g of it in 100 mL of water).
How to Test for Protein –
- Take a small amount of food items.
- Grind it into powder or mash it into a paste.
- Add the ground or mashed food item to a clean test tube.
- Add a few drops of water into the test tube and shake it.
- Add 2-3 drops of copper sulphate solution to the test tube and mix the content of test tube gently.
- Now, add 10-12 drops of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake the test tube and then let it stand for a few minutes.
- Observe the test tube and draw your inferences.
Observations & Inferences –
If the content of the test tube turns violet, then it confirms the presence of protein in our food item.
Test for Fats
Things we need for the test –
- Food items.
- Piece of paper ( preferably white).
How to Test for Fat –
- Take a small quantity of food and wrap it in a piece of white paper.
- mash or crush the food wrapped up in the paper without tearing the paper.
- Straighten the paper remove the food and let the paper dry for some time.
- Observe the paper and draw your inferences.
Observations & Inferences –
An oily patch on paper shows that the food items contained some fat. If it had been just water it would have evaporated from drying.
All food items are not rich in all 7 major nutrients.
What Do Various Nutrients Do for Our Body?
Now that we have learned about the various nutrients, let’s get to know their usages and sources as well.
1. Carbohydrates –
Function: Provide energy to our body.

Sources: Potato, sweet potato, sugarcane, papaya, melon, mango, maize, wheat, bajra, rice etc.
2. Fats –
Function: They also provide us with energy. In fact they provide more energy than carbohydrates of the same amount.
i) Plant-based sources: Coconut oil, mustard oil, sunflower oil, groundnut oil, almond oil, soybean oil, etc.
ii) Animal-based sources: Ghee, butter, milk, cream, eggs, meat, fish, etc.

Carbohydrates and fats are also called ‘Energy giving food’.
3. Proteins –
Function: Helps in the growth, development, and repair of our body. Food that is rich in proteins is also called ‘bodybuilding foods’.
i) Plant-based sources: Gram, peas, moong, toor dal, beans, soybeans, etc.
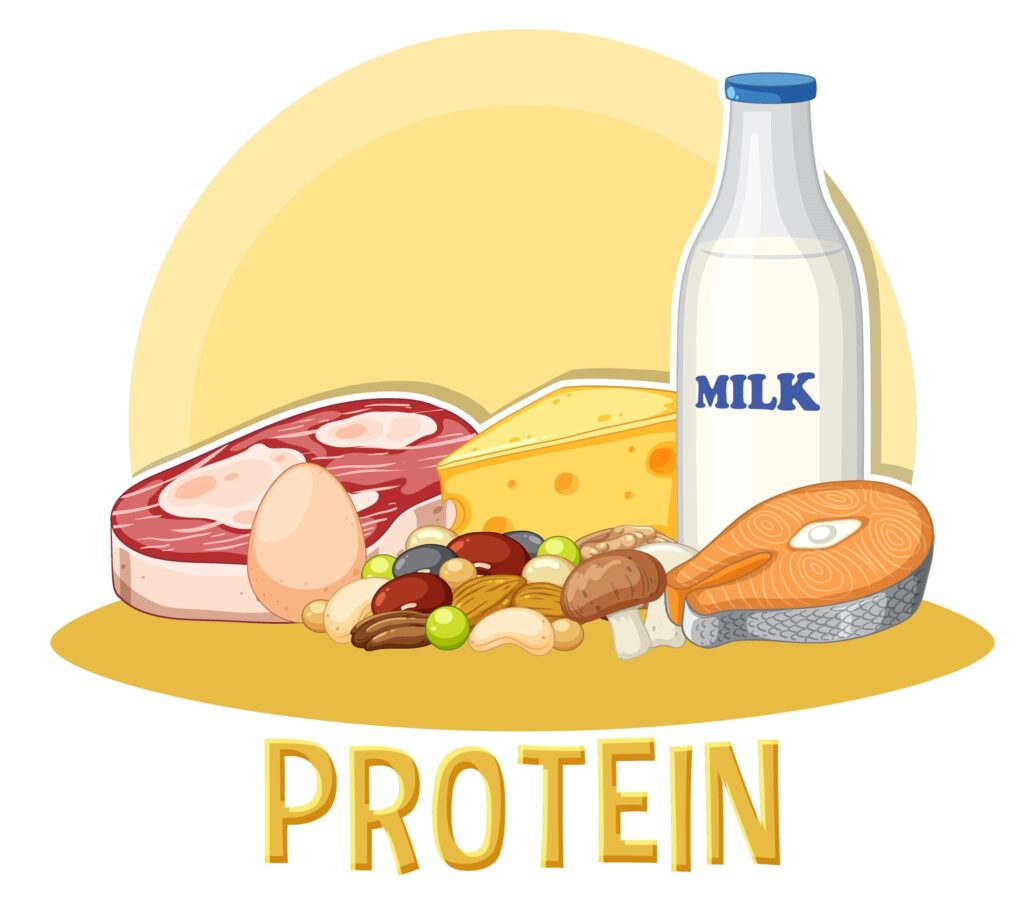
ii) Animal-based sources: Meat, milk, fish, eggs, etc.
4. Vitamins –
There are vast variety of vitamins that we get from our food with each one of them having its specific function.

| Vitamin’s Name | Function of The Vitamin | Sources |
| Vitamin A | Keeps our eyes and skin healthy | Carrot, papaya, mango, milk, fish oil, etc. |
| Vitamin B Complex | Helps our body to convert food into energy. | Meat, rice, wheat, legumes, nuts, etc. |
| Vitamin C | Helps our body to fight against disease and infections. | Orange, tomato, mosambi, lemon, pineapple, amla, guava, green chili, etc. |
| Vitamin D | Helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth | Sunlight, fish, milk, eggs, butter, meat (liver), etc. |
| Vitamin E | Helps to keep our immune system strong against bacteria and viruses | Almonds, pumpkin, spinach, sunflower oil, soybean oil, etc. |
| Vitamin K | Regulates blood clotting | Spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, eggs, meat etc. |
5. Minerals –
Function: These are needed in our body in a very small amount but they are important for the proper growth of the body and for maintaining good health.
Sources: fruits and vegetables, meat, eggs, salt, whole grains, etc.
6. Dietary Fibres or Roughage –
Function: These are important for intestinal health as they help our body to get rid of undigested food.

Sources: plant products like fruits, vegetables, grains, pulses, etc.
7. Water –
Function: Helps our body to absorb nutrients from food, helps in the purification of our body by throwing out waste material such as urine and sweat out of the body, and helps in the regulation of body temperature as well.

Sources: liquid water that we drink, fruits, vegetables, milk, curd, buttermilk, etc.
Balanced Diet
Is a diet that contains all the important nutrients in the right quantity according to a person’s needs.
The amount of nutrients in our diet may vary according to our age, the amount of physical work we do, our gender, etc.
We consume a wide variety of food items just to fulfill our dietary needs as we can’t derive all the important nutrients from just one food item, and hence there is a variety in our food items.
Malnutrition:
is a serious condition that mainly happens when we don’t consume the nutrients in the right amount, and due to this, a person may become underweight (due to the consumption of less energy foods) or overweight or obese (due to overconsumption of high energy foods). Hence, to prevent such conditions from happening we have to have a proper balanced diet.
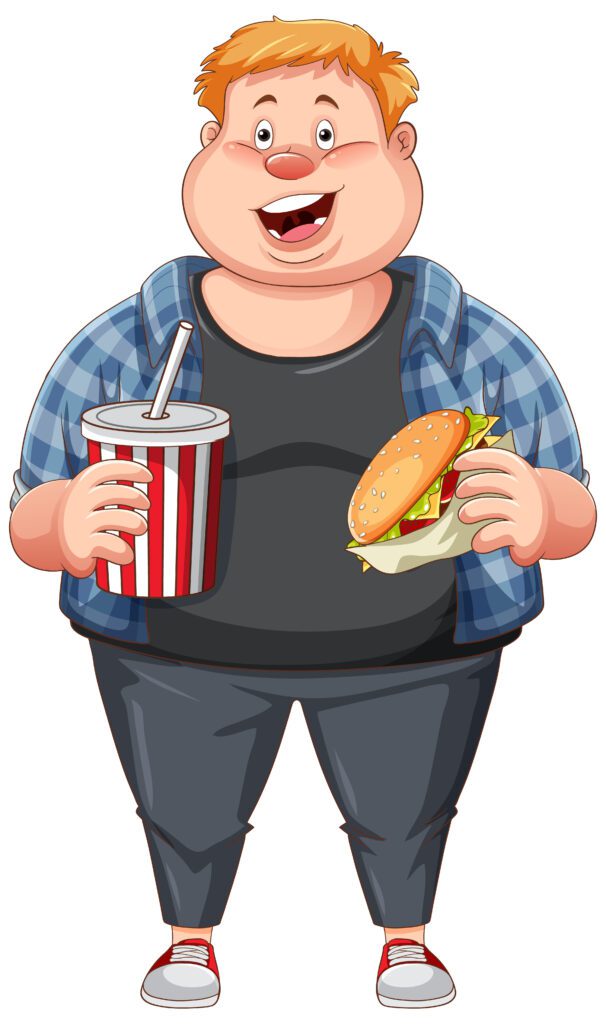

Food should be properly cooked, washed, and consumed to minimize the loss of important nutrients from the food items.
Deficiency Diseases
Deficiency: a condition in which a person is not getting one or more than one essential nutrient from their food for a longer period of time.
Deficiency Disease: caused by the deficiency of nutrients in our food for a longer period of time.
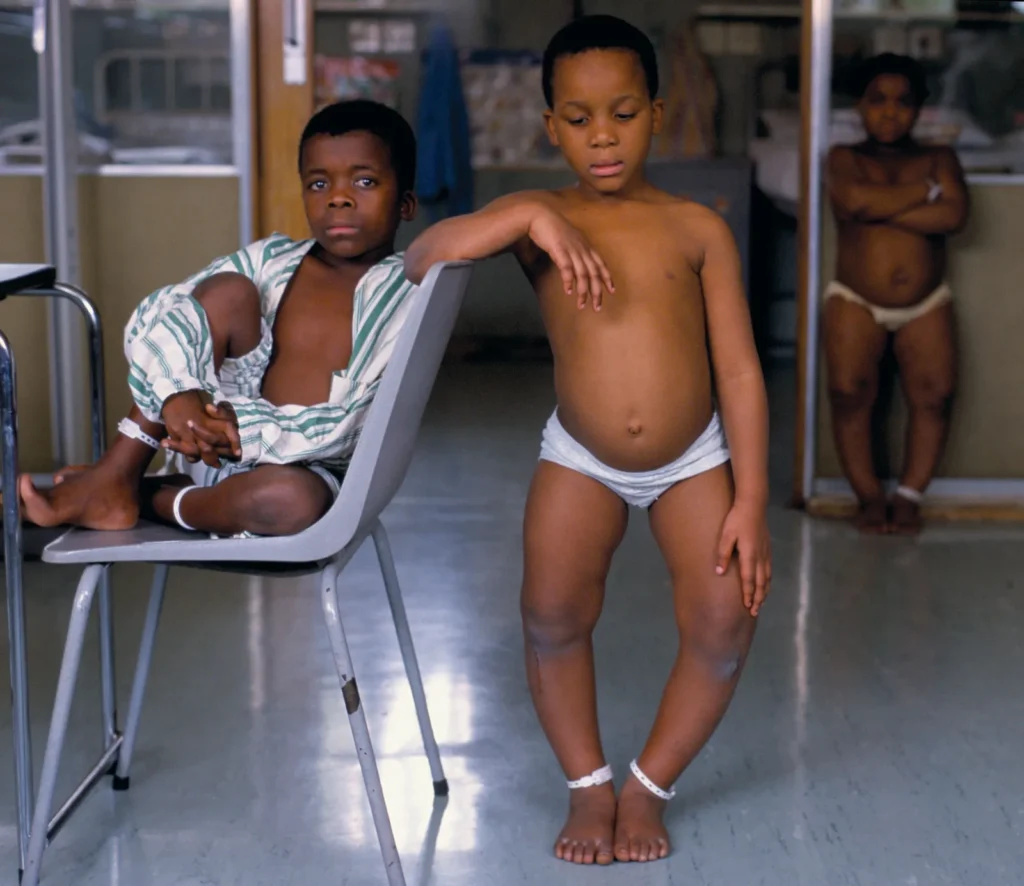
Deficiency of Protein (Kwashiorkor) –
Symptoms: stunted growth, swelling of the body, discoloration of hairs, diarrhea, skin diseases, etc.
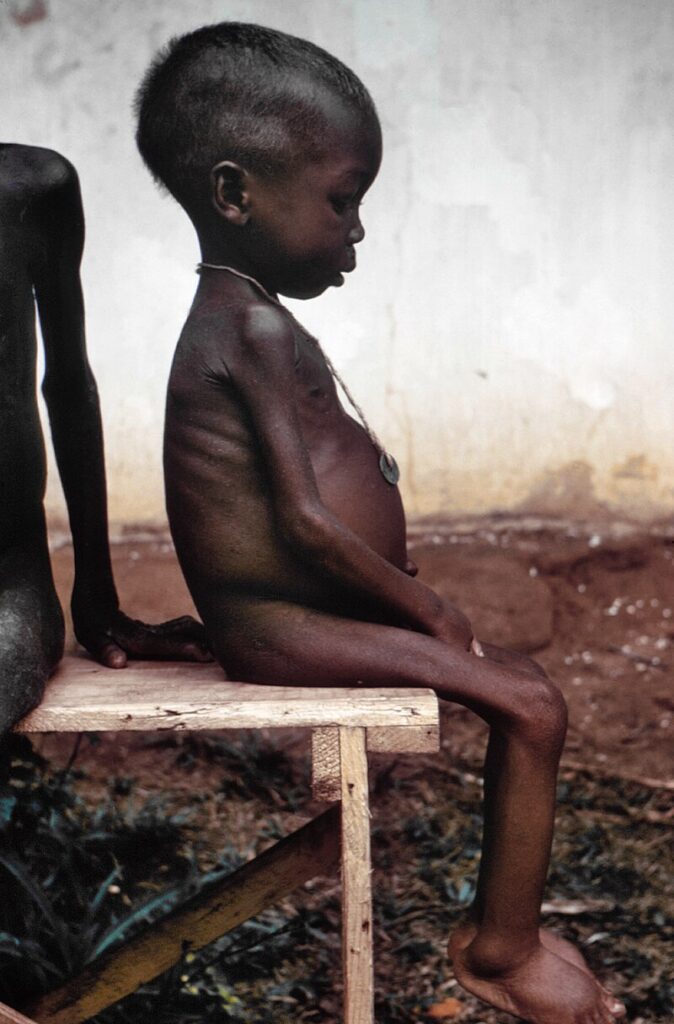
Deficiency of Carbohydrates and Proteins –
Symptoms: growth may stop completely in this case. A person becomes too weak that they may not be able to walk or even stand up. In worst-case scenarios, it may result in death as well.
Deficiency of Fats –
Symptoms: body becomes weak, dry rashes, hair loss, weak immune system, etc.
Deficiency of Vitamins –
| Vitamin’s Name | Deficiency Disease or Disorder | Symptoms |
| Vitamin A | Loss of vision, night blindness | Improper bone development in children as a result bones become weak, soft, and bent. |
| Vitamin B1 | Beriberi | Loss of appetite, weak muscles, pain in the limbs, swollen legs, etc. |
| Vitamin C | Scurvy | Bleeding gums, wounds take longer to heal, anemia, etc. |
| Vitamin D | Rickets | paleness, weakness, fever, dizziness, dark-colored urine, etc. |
| Vitamin E | Hemolytic anemia | paleness, weakness, fever, dizziness, dark colored urine, etc. |
| Vitamin K | Excessive Bleeding | significant bleeding, blood don’t clot |

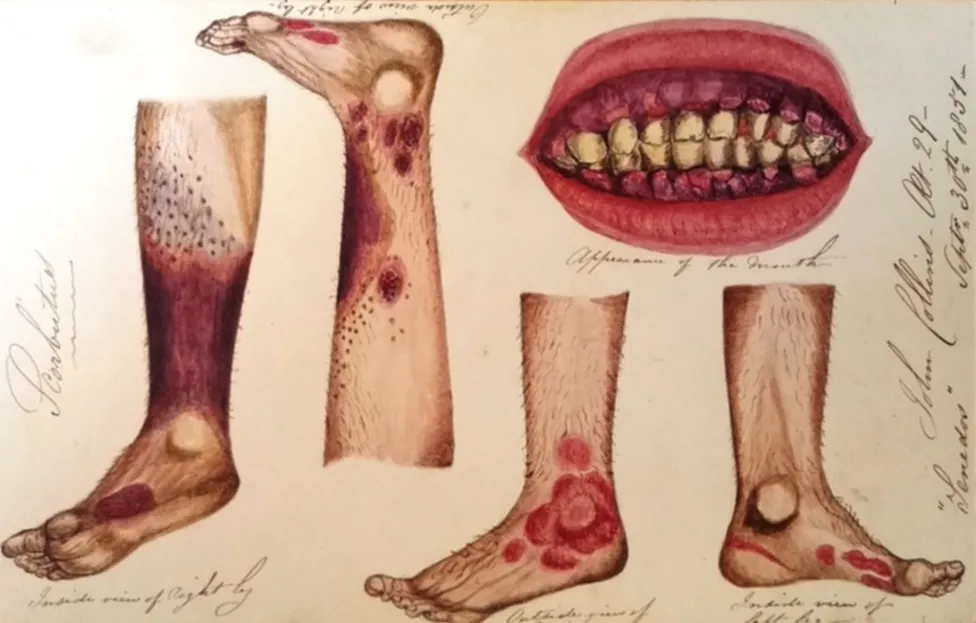
Deficiency of Minerals –
| Mineral | Deficiency Diseases or Disorder | Symptoms |
| Calcium & Phosphorus | Bone and tooth decay | weak bones, less bone density, tooth decay |
| Iodine | Goitre | swelling of the neck just above the chest, intellectual disability |
| Iron | Anemia | weakness, paleness, fever etc. |
Deficiency of Water –
Also known as dehydration.
Symptoms: dry mouth, excessive breathing, extreme thirst, increased heart rate, low blood pressure, a fever, little or no urine, little or no sweat, etc.
Conclusion
A balanced diet is foremost important for a healthy life and prolonged life free from any diseases. The government is also putting efforts into providing proper nutrients to the people via Fortified foods and other schemes as well.
Now, that we have completed this chapter, you can try solving its NCERT Excercise questions and their solutions link has been provided down below.
References & Credits
- Class 6th Science NCERT Textbook
- Image by brgfx on Freepik
- Image by Freepik
- Image by pch.vector on Freepik
Thank You for Choosing Scikshak ❤️