Before starting with Class 6 Science Chapter 8 i.e. ‘Light, Shadows and Reflections’, I am hoping that you have completed the 7th chapter. If not, then you can go through its Notes and NCERT Exercise Solutions whose links have been provided below. ⤵️
Table of Content
Introduction
On your way to school, you see a whole lot of things and beings like buses, cars, people, dogs, cats, crops, etc.
But have you ever wondered, how we can see all these entities?
If you thought with our eyes, then you are partially correct but what enables the eyes to see them? That’s the actual question
What if it is completely dark inside a room, are you still able to see objects and people inside the room?
No. Because there is no LIGHT present there for us to see the objects and people inside the room.
It is the light that is enabling us to see with our eyes.
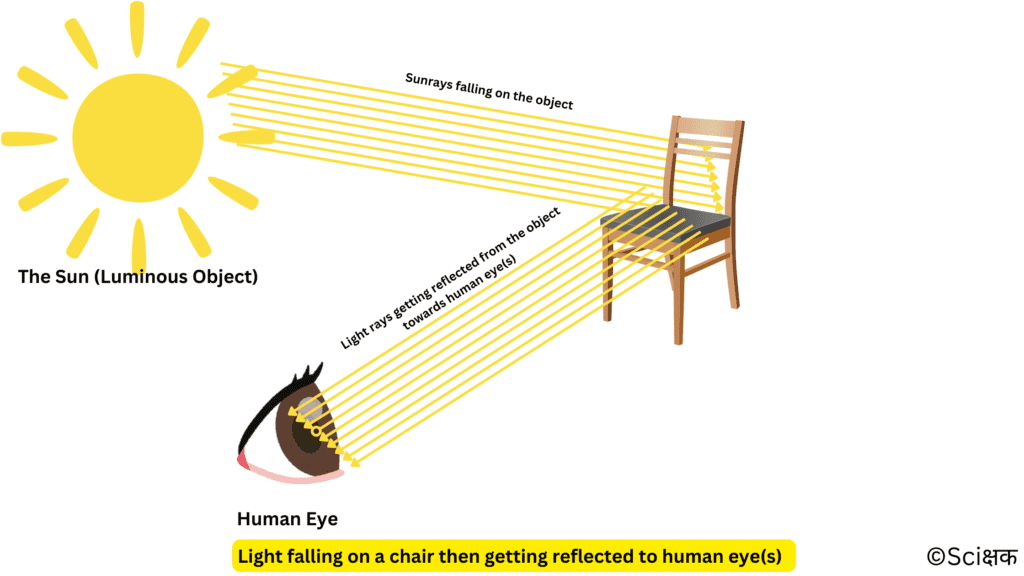
We get light from various objects like the sun, from a torch, from fireflies, etc.
Objects that emit light of their own are known as luminous objects. e.g. like the sun.
How do we see?
We see when light from a luminous object falls on an object and then it travels to our eyes.
Transparency
It is the ability of an object to let the light pass through itself.
We have already understood this concept in detail in Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Notes, you can refer to those. The link has been provided below.
- Objects that allow light to pass through them completely are called transparent. You can see through them clearly. e.g. glass, water, etc.
- Objects that don’t allow light to pass through them are called opaque. You can’t see through them at all and they form shadows. e.g. stone, wood, etc.
- Objects that partially allow the light to pass through them are called translucent. You can see through them partially. e.g. human skin, butter paper, etc.
What are Shadows?
Have you ever noticed a dark patch forming on a surface (ground, wall, etc.) when you go out in sunlight, that looks roughly like you.

A shadow is a dark area obtained on a surface where light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object.
Things required to produce a shadow are:
- An opaque object
- A source of light
- A background or a surface
Shadows give us a rudimentary or rough idea about the shape of an object but sometimes shadows can be deceiving as well.
For example, the shadows of all humans look similar to the shadows of human cardboard, mannequins.
And, the shadow of a rectangular notebook and a rectangular box look the same, etc.
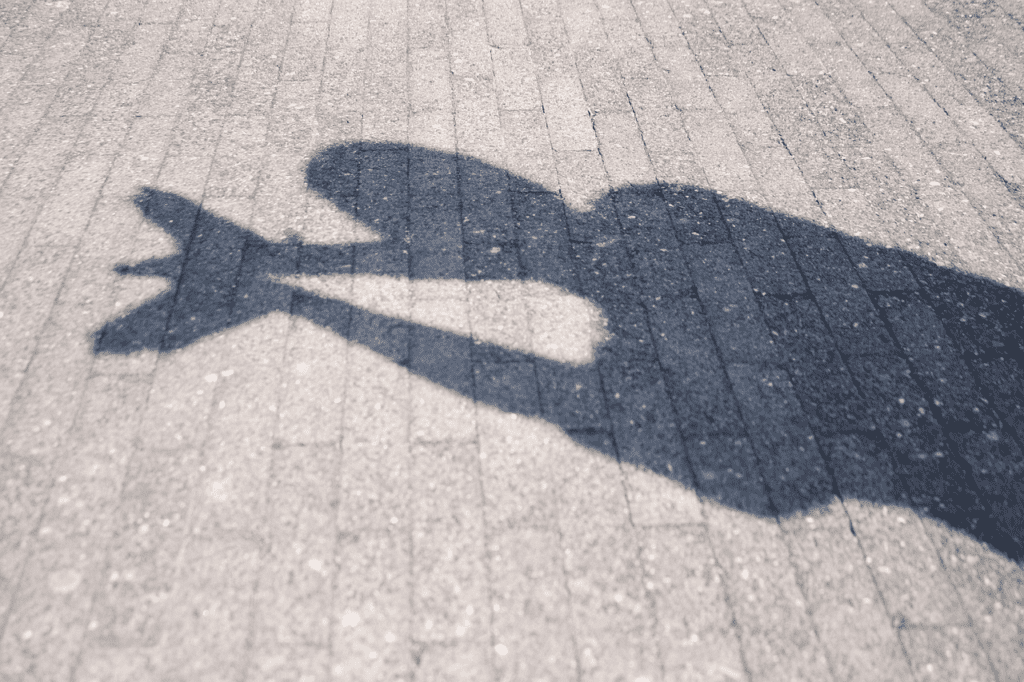

Shadows don’t give us an idea about the colour & odour of an object.
A Pinhole Camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens but with a tiny hole or aperture.
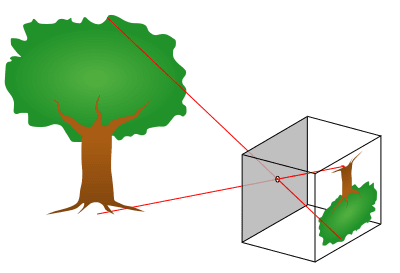
Pinhole camera produces upside-down images of an erect object.
Did you know: There is an interesting pinhole camera in nature that is the tree foliage (leaves). When we pass under a tree in the sunlight, we notice small patches of sunlight on the ground. Well, these small patches of sunlight are actually the pinhole images of the Sun. The small gaps between the leaves act as pinholes.
Does Light Travel in a Straight Path?
The formation of shadows and pinhole images of objects is only possible if light travels in a straight path.
Well, let’s prove this with a short experimental activity.
Activity to Prove that The Light Travels along a Straight Line
- Fix a candle on one end of a table and lit it.
- Take a piece of pipe or a long rubber tube.
- Now, standing a bit farther from the candle try to look at its flame through the pipe.
- Is candle flame visible to you?, Well, Yes it is visible to you.
- Now, bend the pipe and try to look at the candle flame again.
- Are you still able to look at the candle flame through your bent pipe?
- No, we are not able to look at the candle flame through the bent pipe because the light from the candle got obstructed by the bend.
Hence, proved that light travels in a straight path.
Mirrors and Reflections
We all use mirrors in our daily lives to look at ourselves to comb our hair properly, to look at the vehicles behind us on a road, etc.
Well, your face in a mirror is actually a reflection of yourself.
Reflection is the bouncing off light from an object whose surface is smooth and shiny like a mirror, water, metallic surfaces, etc.
Mirrors can change the direction of light that falls on it.
The above videos give us an idea about the manner in which light travels and gets reflected off a mirror.
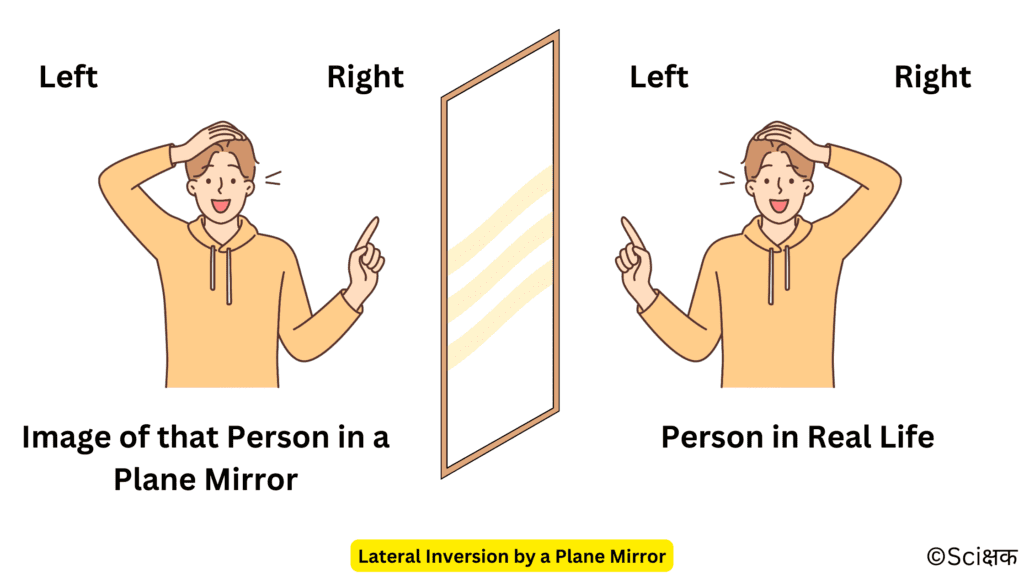
What Type of an Image is Formed by a Plane Mirror?
Plane mirrors form laterally inverted (which means it turns the left side into the right side and the right side into the left side) images.
A Periscope
It is a device that uses reflections to see around the corners.
The image formed by a periscope is not laterally inverted as it has two plane mirrors so they cancel out the lateral inversion effect of each other and give us the original image of the object.
Fun Fact: If you can see someone in a plane mirror’s image then they can see you as well in that image.
References & Credits
- Class 6 Science NCERT Textbook
- Image by Misael Silvera from Pixabay
- Image by Karen Brugman from Pixabay
- https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/resources/48-reflection-of-light
- Image by Warren Griffiths from Pixabay
- Image by freepik
Thank You for Choosing Sciक्षक ❤️